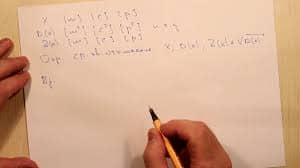It is Monday/July 23/1992 It is £5.50 Tom is 14
10.9.5 'Be' + possessives
It's mine/Tom's. They are mine/Tom's
10.9.6 'Be' + adverbs and prepositional phrases [> 7. 3.3]
She is here/there They are upstairs
The play is next Wednesday (future reference)
He is in the kitchen They are at the door
10.9.7 'Be' + adverb particle and 'home' [compare > 8.29.2, 10.13.4]
Be combines with adverb particles (away in out, etc. [> 8.4]);
Is Tim in? No, he's out He's back in an hour Be combines with home [at is optional):
Where was Tim? Was he home?/Was he at home?
Compare: Tim's home now (= he has arrived at his home)
Tim's at home now (= he may not have left home at all)
10.9.8 'Be' in the present and past replacing 'have/had'
In informal English, the present and past of be can replace have/had [present and past perfect, > 9.22, 9.28] with verbs like do, finish, go. I'm done with all that nonsense (= I have done, i.e. finished)
/ left my keys just there and next moment they were (had) gone Have you finished with the paper? - I'm (have) nearly finished
10.9.9 'Empty subject' + 'be' [> 4. 12]
It's foggy It's 20 miles to London
10.9.10 'Be' + infinitive [> 9.47-48, 16.16]
My aim is to start up my own company
'Be' as a full verb
10.10 Form of the present and past progressive of 'be'
| present progressive | past progressive | ||||
| / am | (I'm) | being | I | was | being |
| You are | (You're) | being | You | were | being |
| He is | (He's) | being | He | was | being |
| She is | (She's) | being silly | She | was | being |
| (It is | (It's) | being) | (It | was | being) |
| We are | (We're) | being | We | were | being |
| You are | (You're) | being | You | were | being |
| They are | (They re) | being | They | were | being |
The forms He s being silly and He s been silly [> 10.12] should not be confused
|
|
|
10.11 The use of 'be' + 'being' to describe temporary behaviour
The progressive forms normally occur only with the present and the past forms of be. They are used with a few adjectives and nouns [> App 41] (or adjective and noun combinations). The progressive is possible with adjectives such as naughty silly, referring to passing behaviour, but is not possible with adjectives describing states (hungry, thirsty, etc.) With some combinations there is a strong implication that the behaviour is deliberate. Compare temporary and usual behaviour in the following:
Your brother is being very annoying this evening
He isn't usually so annoying
Your brother was being a (silly) fool yesterday
He isn't usually such a (silly) fool
10.12 Form of the present perfect and past perfect of 'be'
| present perfect | past perfect | |||
| full form | short form | full form | short form | |
| / have been | I ve | been ' | I had been | I'd been |
| You have been | You ve | been | You had been | You'd been |
| He has been | He's | been | He had been | He'd been |
| She has been | She s | been ill She had been | She'd been | |
| (It has been) | (Its | been) | (It had been) | |
| We have been | We ve | been | We had been | We'd been |
| You have been | You ve | been | You had been | You'd been |
| They have been | They've | been | They had been | They'd been |
The forms He s been silly and He s being silly [> 10 10] should not be confused.
10.13 Uses of 'have been' and 'had been' [compare > 9 24]
In many of the uses described below, other languages require the present or past of be where English requires has been or had been.
10.13.1 'Have been/had been' + adjective: behaviour and states
Have been and had been will combine not only with adjectives describing temporary behaviour (annoying, etc., [> 10.11]), but also with those describing states and moods continuing up till now or till
10 Be, Have, Do
then. Have been is common in conversation and had been in reported speech and written narrative:
Behaviour: She's been very quiet I said she had been very quiet States: / ve never been so tired I said I'd never been so tired Moods: He's been very gloomy I said he d been very gloomy
Some participles used as adjectives combine with have/had been: My uncle has been retired for more than two years Their dog has been missing for three days
And notice especially: She's been gone (= away) for half an hour
10.13.2 'Have been/had been' + adjective: weather, etc.
Have been and had been also combine with adjectives describing the
weather (i.e. states):
It's been very cold lately I said it had been very cold
In certain contexts other adjectives (e.g. numbers) are possible: You're speaking as if you'd never been 15 years old in your life
|
|
|
10.13.3 'Have been/had been' + noun: professions, behaviour
Have been and had been will combine with noun (or with adjective + noun) to ask about or describe professions:
 2015-08-21
2015-08-21 383
383