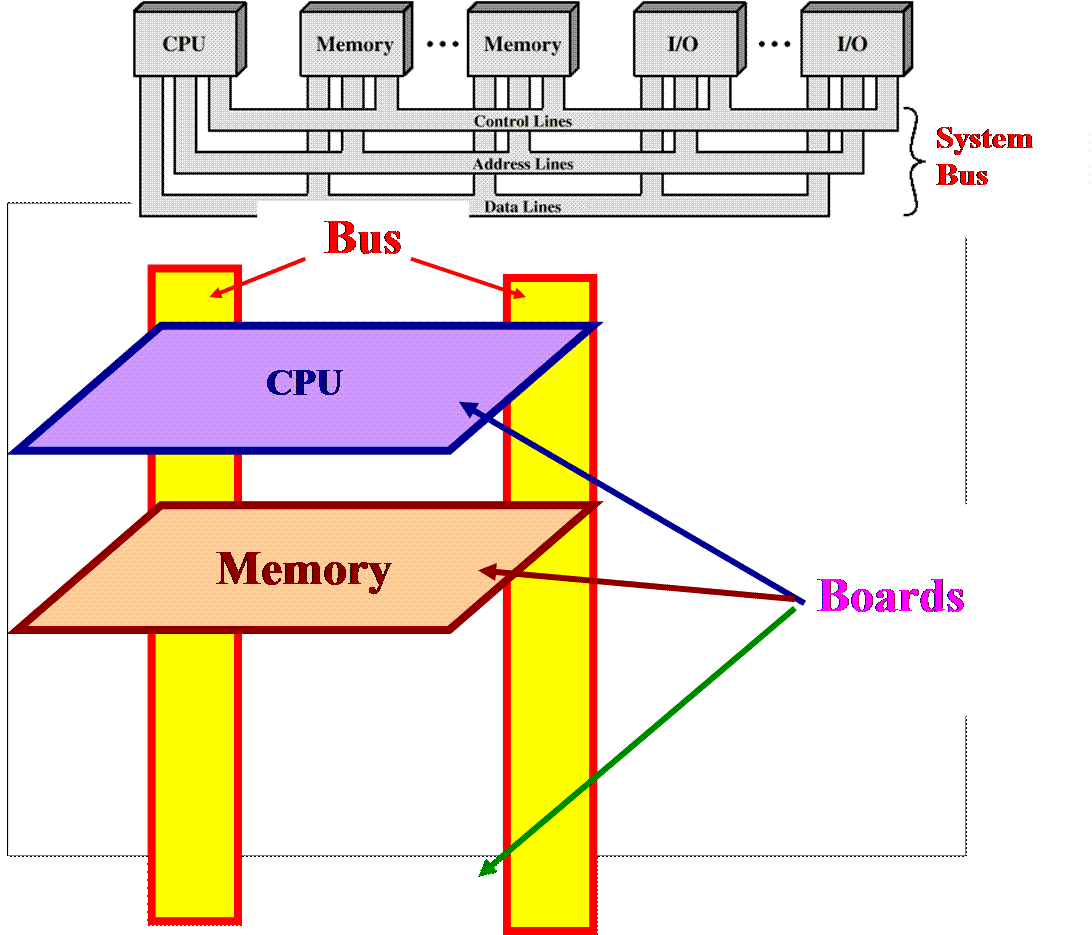
A bus that connects major computer components (CPU, Memory, I/O) is called a System Bus.
| |||
 |

| |||||
 | |||||
 |
z
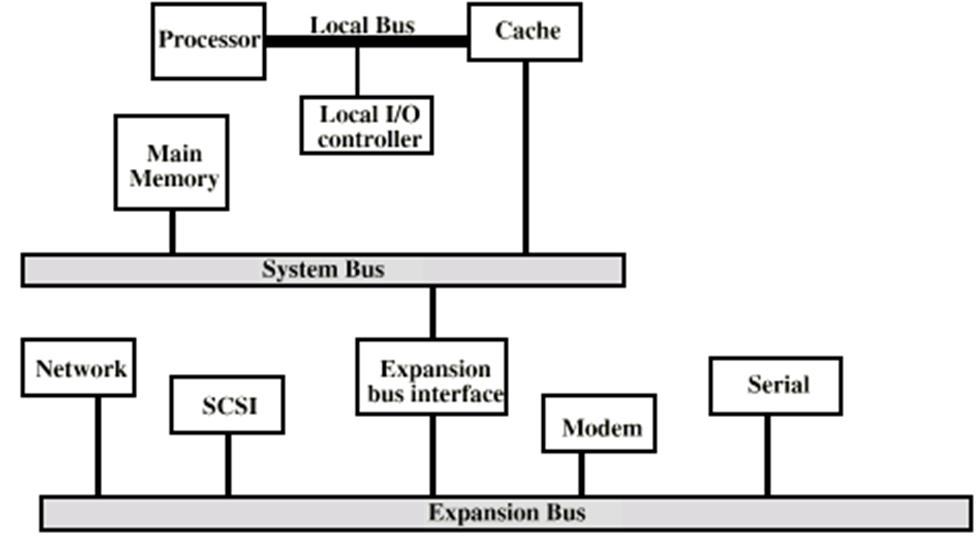
Up to now the Traditional Bus Architecture has been widely used. In this case the Computer System includes Local Bus, which connects the CPU, Cache Memory and some peripheral devices. Cache Memory Controller provides connections not only with the Local Bus, but with the System Bus as well (all modules of the Main Memory are connected with the System Bus). Under such structure all processes of input-output are realized through the System Bus omitting the CPU, it allows the CPU to perform more important operations.
The connecting peripheral devices not directly to the System Bus, but to additional bus - Expansion Bus, which buffers data circulating between the Main Memory and peripheral devices’ controllers allows to support a large variety of external devices, and at the same time to separate information-flows “CPU – Memory” and “ Memory – I/O Controllers”.
The appearance of new high-performance external devices demands to increase speed of data transfer through buses, that is why one more High-Speed Bus is often used in contemporary computer systems. This bus unites high-speed external devices and is connected with the System Bus through special concordance module (модуль согласования) - Bridge. Such kind of structure is called Mezzanine Architecture (Мезонинная Архитектура).
The advantage of this structure: high-speed peripheral devices are integrated with the processor and at the same time they may work independently (themselves). It means that functioning of the bus doesn’t depend on the CPU architecture and vice versa.
До сих пор традиционная архитектура шины широко используются. В этом случае компьютерная система включает в себя местную шину, которая соединяет процессор, кэш-памяти и периферийных устройств. Контроллер кэш-памяти обеспечивает связь не только с локальной шиной, но и с системной шиной, а также (все модули оперативной памяти связаны с системной шиной). При такой структуре все процессы ввода-вывода осуществляется через системную шину, минуя центральный процессор, что позволяет процессору для выполнения более важных операций.
Подключения периферийных устройств не непосредственно к системной шине, но и дополнительные шины расширения, которые буферов данных, циркулирующих между оперативной памятью и контроллерами периферийных устройств "позволяет поддерживать большое количество разнообразных внешних устройств, и в то же время отдельные информация -потоков "CPU - Memory" и "Память - I / O контроллер".
Появление новых высокопроизводительных внешних устройств требует, чтобы увеличить скорость передачи данных через автобусы, поэтому еще одна высокоскоростная шина часто используется в современных компьютерных системах. Эта шина объединяет высокоскоростные внешние устройства и связана с системной шиной через специальный модуль согласования (модуль согласования) - мост. Такая структура называется Мезонинной архитектурой.
Преимущество этой структуры: высокоскоростные периферийные устройства интегрированы с процессором и в то же время они могут работать самостоятельно (сами). Это означает, что функционирование шины не зависят от архитектуры процессора и наоборот.
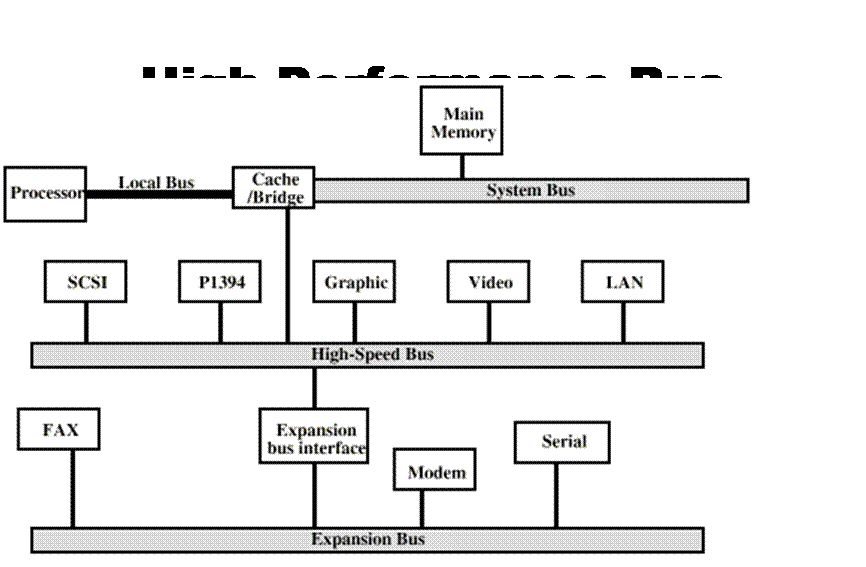
SCSI- Small Computer System Interface; LAN – Local Area Network; PI394 – Peripheral Interface (high-speed)
Bus Types
z Dedicated
§ Separate data & address lines
z Multiplexed
v Shared Lines
v Address valid or Data valid control lines
v Advantage – fewer lines
v Disadvantages
q More complex control
q Reduction in performance
z Physically Dedicated
§ The use of multiple buses, each of which may connect only some certain modules (Expansion Bus, High-Speed Bus)
§ Advantage – high throughput (there is less bus connection)
§ Disadvantage – increased size and cost of the system.
 | |||
 |
| |||
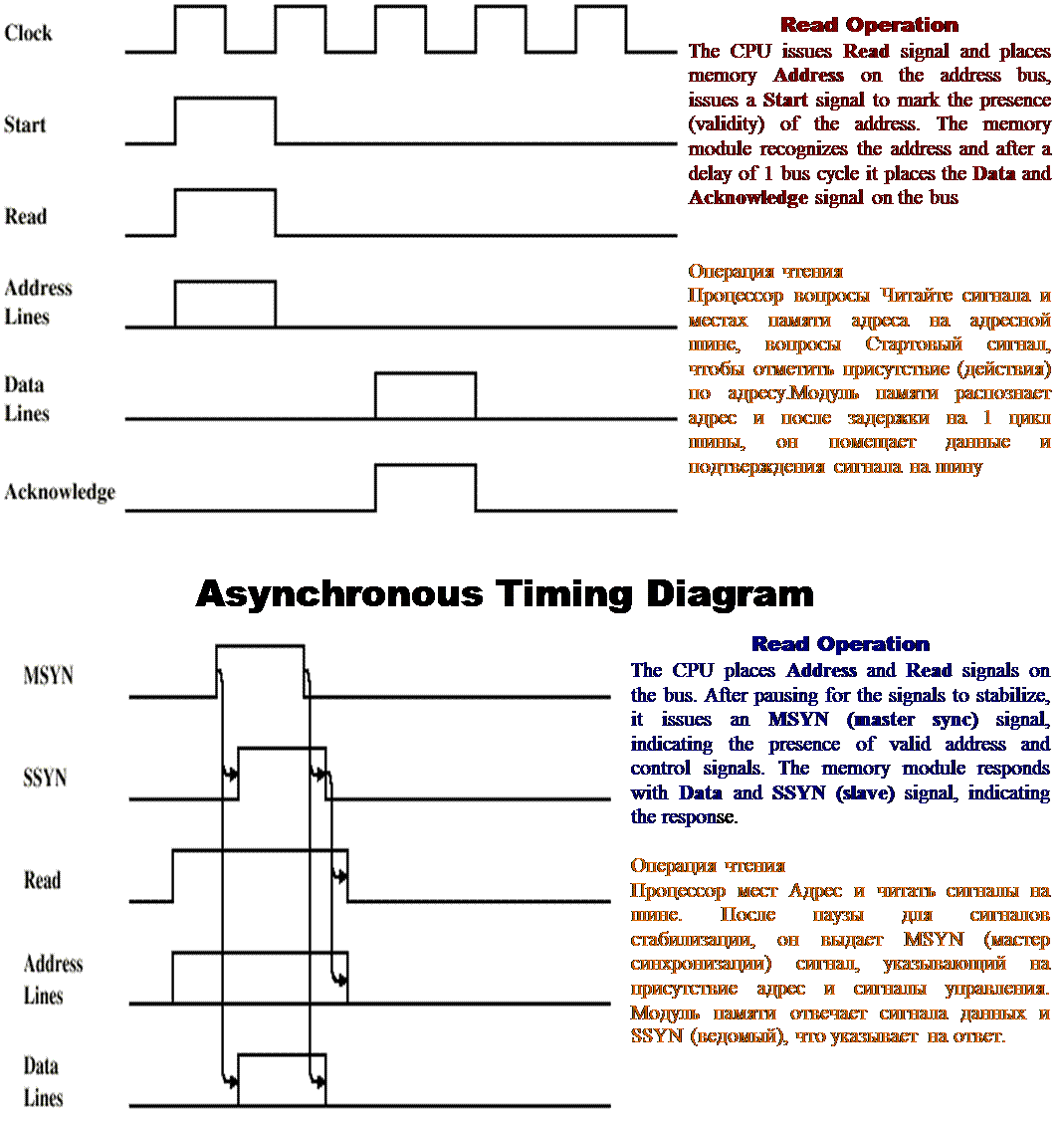 |
Ø Timing refers to the way in which events are coordinated on the bus.
Ø With synchronous timing the occurrence of events on the bus is determined by a clock.
The bus includes a clock line upon which a clock transmits a regular sequence of alternating 1s and 0s of equal duration. A single 1-0 transmission is referred to as a clock cycle (bus cycle) and defines a time slot (интервал). All other devices on the bus can read the clock line, and all events start at the beginning of a clock cycle. Other bus signals may change at the leading edge of the clock signal.
Шина включает в себя часы линии, на которой часы передает регулярные последовательности чередующихся 1 и 0 равной продолжительности. Один 1-0 передача называется тактовый цикл (цикл шины) и определяет интервал времени (интервал). Все другие устройства на шине может читать часами линию, и все события начинаются в начале такта. Другие сигналы шины могут измениться в передний край тактового сигнала.
 2014-02-02
2014-02-02 362
362








